WAN Technology
Wide Area Networks (WANs) are computer networks that cover a large geographical area, often spanning multiple cities or even countries. They are used by organizations to connect their remote offices and employees to each other, as well as to the Internet and other external networks.
In this PDF, we will provide an explanation of WAN technology, including its key components and operational procedures. We will begin by examining the basic principles of WANs and their advantages over other types of networks, such as Local Area Networks (LANs).
We will then delve into the specifics of WAN technology, including its various types, such as Circuit-Switched WANs, Packet-Switched WANs, and Cell-Switched WANs. We will also explore the different WAN topologies, such as Point-to-Point and Multipoint, and the benefits that they offer.
Finally, we will look at some of the challenges facing WAN technology in the modern era, including the need for greater security and reliability, and the rise of new technologies such as Software-Defined WANs (SD-WANs) and 5G networks.
Overview of WAN Technology PDF
Overall, this PDF provides a comprehensive explanation of WAN technology, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses and exploring the future of this important technology.




Book Content
- Circuit Switching
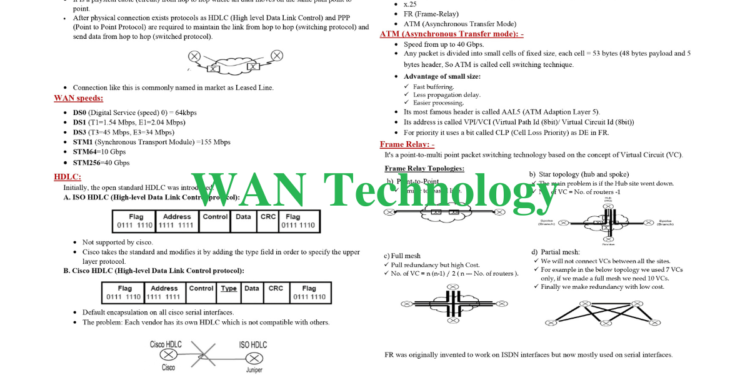
- WAN speeds
- HDLC
- PPP (Point-to-point protocol)
- Configuration
- Packet Switching
- x.25
- FR (Frame-Relay)
- ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
- PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet)
- Label Switching
- IP Forwarding
- MPLS
Book Format:-
To Download PDF:-
For Other Network Books From here