Cisco SD-WAN: Introduction to The Service Level Agreement (SLA)
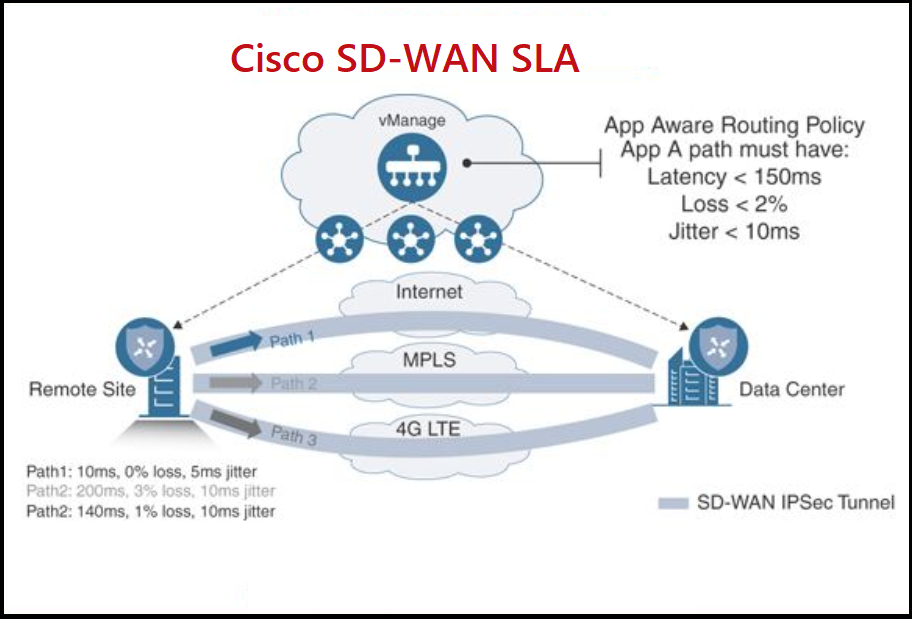
The Service Level Agreement (SLA) in Cisco SD-WAN is an agreement between the service provider and the customer that defines the level of service provided by the service provider to the customer. SLA can include several criteria such as service availability, transport speed, latency, Quality of Service (QoS), and more. SLAs typically include performance standards and responsibilities related to responding to any service-related issues.
SLA helps simplify the relationship between the service provider and the customer and provides a standard for measuring service performance. It also defines mutual responsibilities and commitments between the parties, ensuring the delivery of premium service to the customer.
When a traffic flow is matched to an SLA class, the Cisco SD-WAN solution applies a specific set of policies and actions to that flow, such as:
- Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize and shape the traffic
- Path selection policies to determine the best path for the traffic to take through the network
- Performance monitoring policies to measure the end-to-end performance of the traffic
SLA Parameters
SLA classes can be configured using a variety of parameters, including:
- Bandwidth
- Latency
- Priority
- Jitter
Bandwidth:
Administrators can assign different maximum and minimum bandwidth limits to different SLA classes to ensure that critical traffic always has enough bandwidth available.
Latency:
Administrators can assign different latency thresholds to different SLA classes to ensure that critical traffic is always given priority and experiences low latency.
Priority:
Administrators can assign different priority levels to different SLA classes to ensure that critical traffic is always given priority over less-important traffic.
Jitter:
Administrators can assign different jitter thresholds to different SLA classes to ensure that critical traffic is given priority and suffers low jitter.
When configuring SLA classes in Cisco SD-WAN, administrators can assign different classes of service to different types of traffic, such as traffic to the cloud, traffic to specific sites, or traffic to specific applications.
This allows them to ensure that all traffic is given the appropriate level of service based on its priority, and to manage bandwidth and performance more effectively.
It’s worth mentioning that the Cloud Onramp feature on Cisco SD-WAN also allows administrators to select the cloud service providers (CSPs) and the appropriate VPN to reach them, as well as routing and traffic engineering options, in this way administrators can make sure that their traffic reaches the cloud in the most efficient and secure way possible.
Conclusion:-
the SLA class in Cisco SD-WAN Cloud Onramp enables administrators to specify a level of service and set a priority for traffic moving to SaaS services and the cloud, ensuring that it is provided with the necessary performance, dependability, and security.